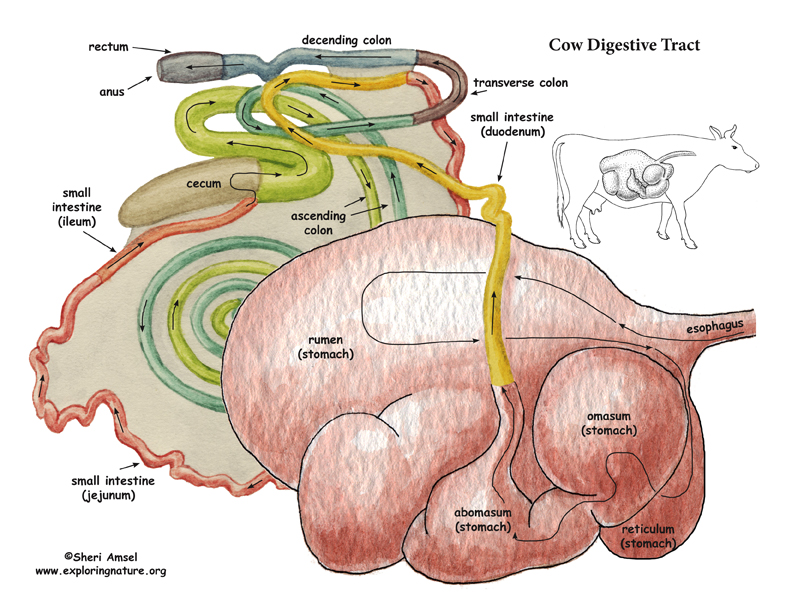
Cow Digestive Tract
Unique Anatomy of a Cow's Digestive System. Cattle belong to a category of animals called ruminants. Unlike monogastric animals like humans, ruminants have a four-compartment stomach: the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum. Each chamber has a specific function in the digestion and fermentation of forage and grains.
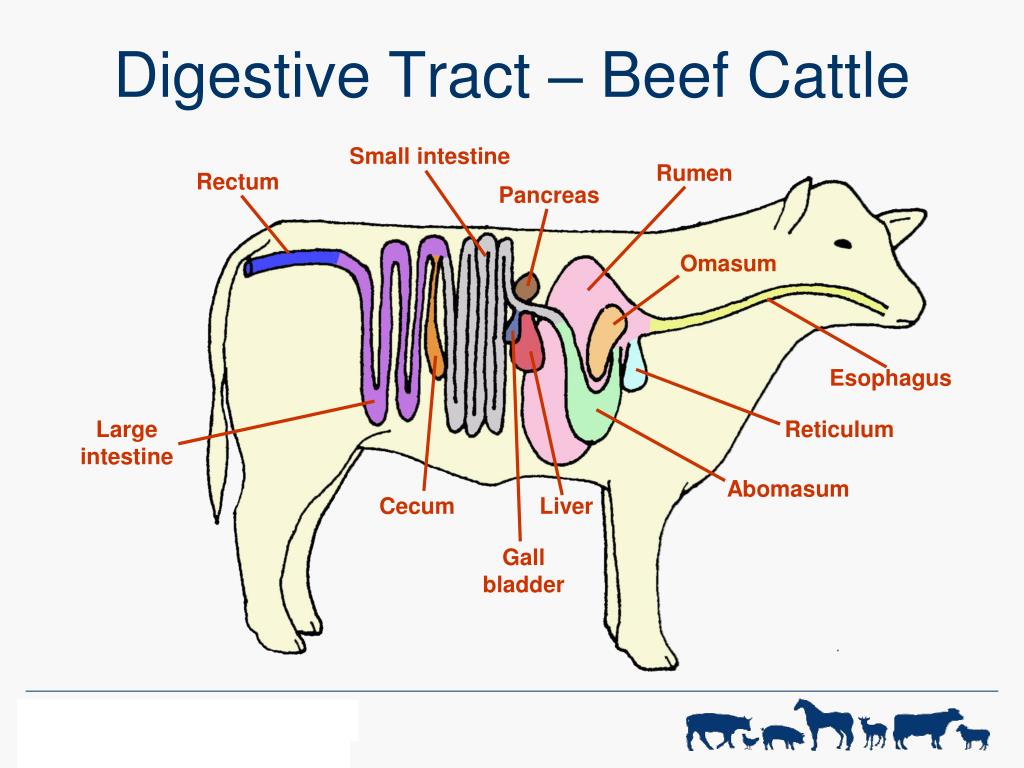
PPT Digestive Physiology of Farm Animals PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3835894
The animated 3D cow allows you to see inside a cow and view from different angles using your mouse or finger - find out more about cows amazing digestive system, milk production, heart and liver. View The Amazing Cow interactive. Have a look at DairyNZ's FeedRight resources for a more in-depth look at ruminant digestion.

Digestive System of a Cow
FIGURE 3. A basic diagram of the digestive system of a cow. Feed conversion and rate of gain in a ruminant are strongly affected by the type and number of microorganisms in the rumen. The rumen must contain the appropriate proportions of cer-tain types of microorganisms to maximize productivity. For example, it is believed that proto-

Livestock Digestive System Livestock Cattle
The cow stomach anatomy comprises four compartments - rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum. Here, I will focus on the anatomical facts of these four compartments of cow compound stomachs with a diagram. Quick overview: rumen is the larger and more capacious compartment than the reticulum, omasum, and abomasum of a cow's stomach.
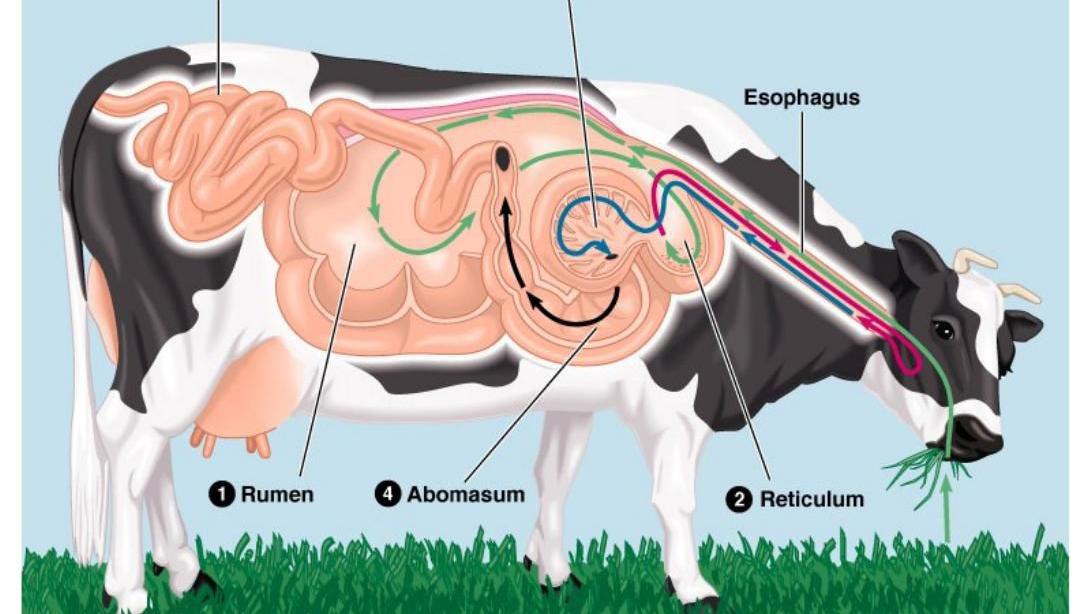
Cow digestive system
The cow has the stomach volume and properties necessary to assist with the microbial digestion. The ruminant digestive tract and the ruminant stomach are shown in Figure 1. The ruminant stomach is divided into four compartments: the rumen, reticulum, omasum and abomasum. Digesta can flow freely between the first two compartments, the rumen and.
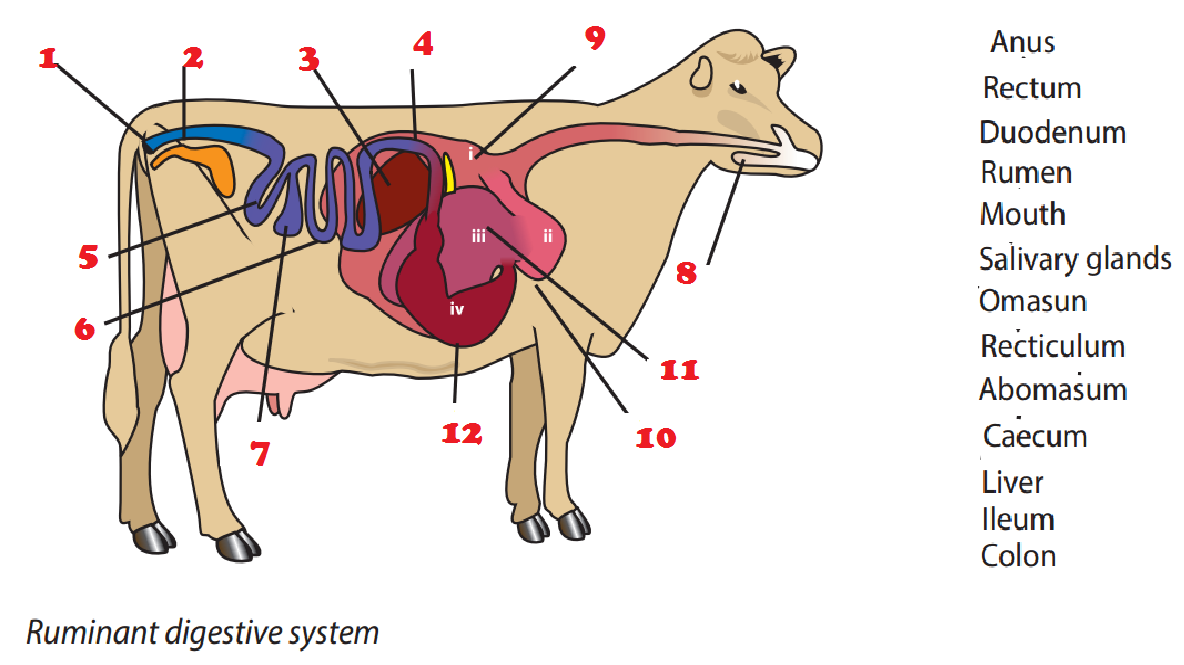
Magh Ag Sci Ruminant Digestion
The cow digestive system diagram might help you to understand the organs from the mouth to the last part of the large intestine. All the ruminant digestive system's main organs possess unique anatomical facts that differ from other animals. The surface and topographic location of the accessory organs of the cow's digestive system are essential.
Anatomy of the cow digestion digestive Stock Photo, Royalty Free Image 34975817 Alamy
Ruminant stomachs have four compartments: the rumen, the reticulum, the omasum and the abomasum. Rumen microbes ferment feed and produce volatile fatty acids, which is the cow's main energy source. Rumen microbes also produce B vitamins, vitamin K and amino acids. In calves, the esophageal grooves allows milk to bypass the rumen and directly.

Draw The Digestive Tract Of A Cow All About Cow Photos
A cow's digestive system consists of 6 components: mouth, esophagus, 4 compartment stomach, small intestine, cecum, and large intestine. The 4 compartments of the stomach are the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum. A cow is a ruminant, which means that it is set apart from other animals because of its complex digestive systems.
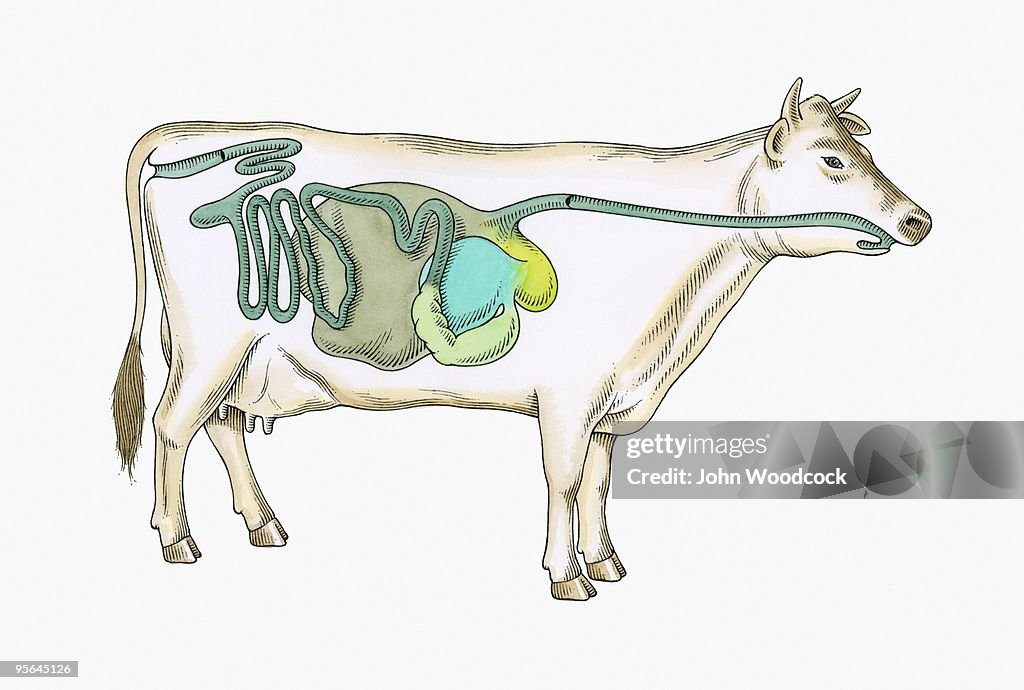
Cross Section Illustration Of Digestive System Of Cow HighRes Vector Graphic Getty Images
Ruminants are hoofed mammals that have a unique digestive system that allows them to better use energy from fibrous plant material than other herbivores. Unlike monogastrics such as swine and poultry, ruminants have a digestive system designed to ferment feedstuffs and provide precursors for energy for the animal to use.

Cow's digestive system by Angela Salvato Cow digestive system, Large animal vet, Animal science
The digestive system of a cow consists of the mouth, lips, esophagus, pharynx, stomach, small and large intestine, and some accessory digestive glands. In addition, the organs from the respiratory system of a cow - consist of the larynx, trachea, and lung. Digestive organs of a cow In a cow, the lips are thick and comparatively immobile.

Ruminant Animals and Rumination Jotscroll
A cow briefly chews food as she eats, breaking it into smaller particles. As she chews, digestive enzymes in her saliva are mixed with the food before it passes down the esophagus into the reticulum and rumen. ( Figure 1 shows the ruminant digestive tract in comparison to the monogastric digestive system). Since digesta flows freely between the.

The Cow Digestive System
Cows 101: Ruminant Anatomy. The cow's digestive tract consists of the mouth, esophagus, a complex four-compartment stomach, small intestine and large intestine (figure 1). The stomach includes the rumen or paunch, reticulum or "honeycomb," the omasum or "manyplies," and the abomasum or "true stomach." The rumen.

Livestock Digestive System Livestock Cattle
These glands release hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes, needed to breakdown feeds. The abomasum is similar to a nonruminant stomach. Rumination . Cows may spend 35 to 40 percent of each day ruminating (cud chewing). The amount of time spent ruminating depends on the diet. Little ruminating occurs when cows eat grain or finely ground rations.

Cow Description, Heifer, & Facts Britannica
Start studying Digestive system of a cow. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-96168548-5c32792046e0fb00010080f9.jpg)
The 12 Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions
In this interactive, you can label parts of the cow's digestive passage. Use your mouse or finger to hover over a box to highlight the body part to be named. Drag and drop the text labels onto the boxes next to the simplified diagram of a cow's digestive system. If you want to redo an answer, click on the box and the answer will go back to.
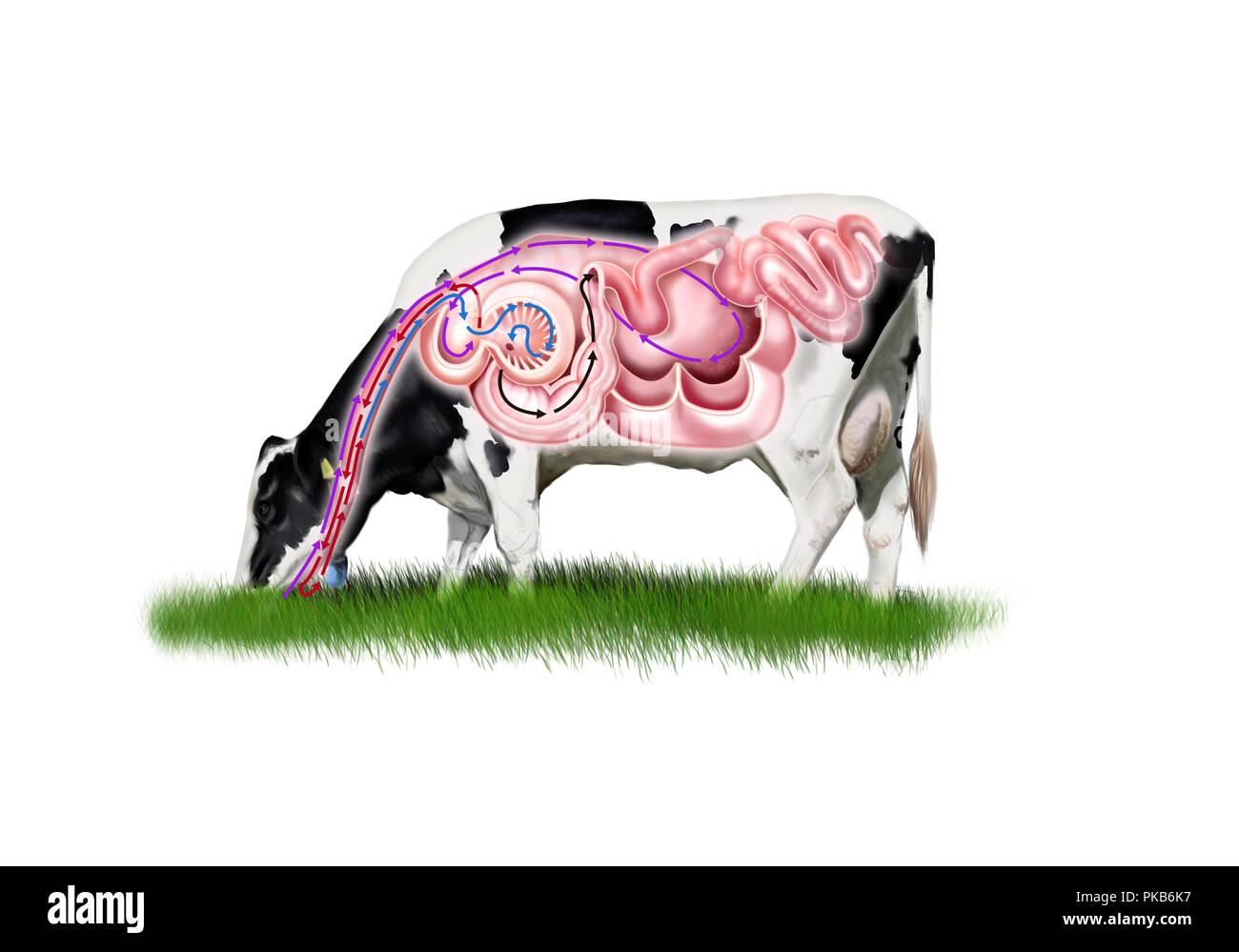

Digital illustration of a cow digestive system Stock Photo Alamy
The main difference between man and cow - besides having two more legs and eating only grass - lies in the cow's stomach. Cows have a ruminant system with four distinctive sections: the rumen, the reticulum, the omasum and the abomasum, while humans have a monogastric stomach with one chamber. The cow digestive system allows herbivores to graze and consume grass until they are full.